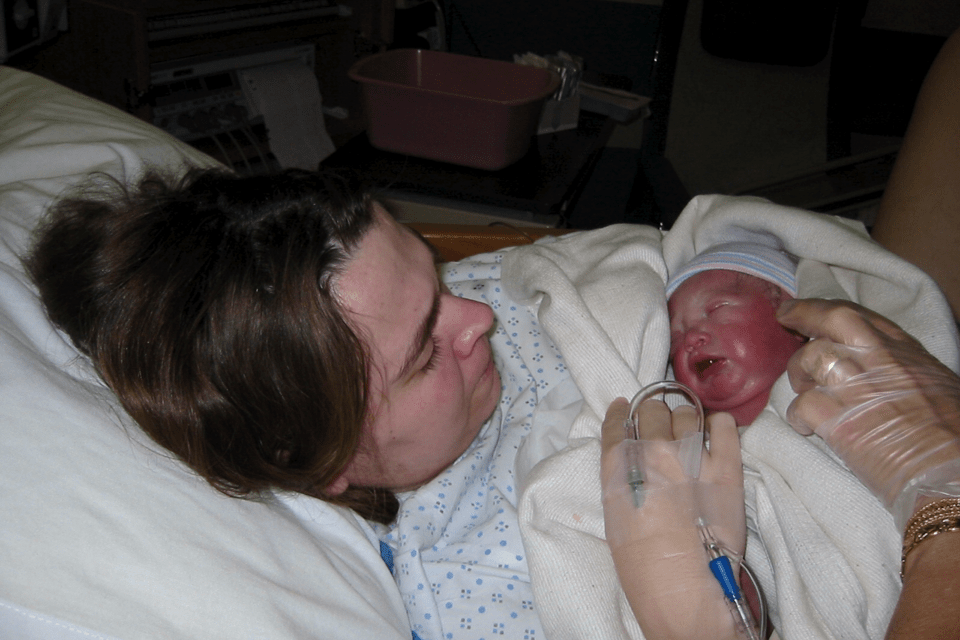
Numerous complications can result from HG if it is severe, not adequately treated, or there is a delay in medical interventions. Life-threatening complications such as a ruptured esophagus (throat) and Wernicke’s encephalopathy may occur after just 2-3 weeks of repetitive vomiting and malnutrition. HG is also a leading cause of premature birth, a 4-fold increased risk.
Long-term health problems have not been studied by many researchers thus far. Our research finds many health issues occurring before and after HG. Many postpartum issues are related to the severity of malnutrition and vomiting; thus, women with excessive, uncontrolled symptoms for months will have a greater chance of complications.
Fetal Effects
A few studies find prolonged stress, malnutrition and dehydration in the mother can put the unborn child at risk for chronic disease (e.g. diabetes, heart disease) in later life. This has been termed fetal or prenatal programming by researchers and few studies have looked at this specifically in HG women.
Our research consistently finds more severe symptoms with weight loss over 10-15% (of prepregnancy) increase the risk of complications in both mother and child, especially if the mother receives little or no medical treatment.
Mothers with more aggressive medical care tend to experience fewer health complications. In children, potential health problems include neurodevelopmental delays and behavioral, emotional and sensory issues. Other factors such as the child's later health habits (e.g. smoking, obesity, diet) also impact development of chronic health conditions. This underscores the importance of providing a mother with the care she needs, for her health and that of her baby.
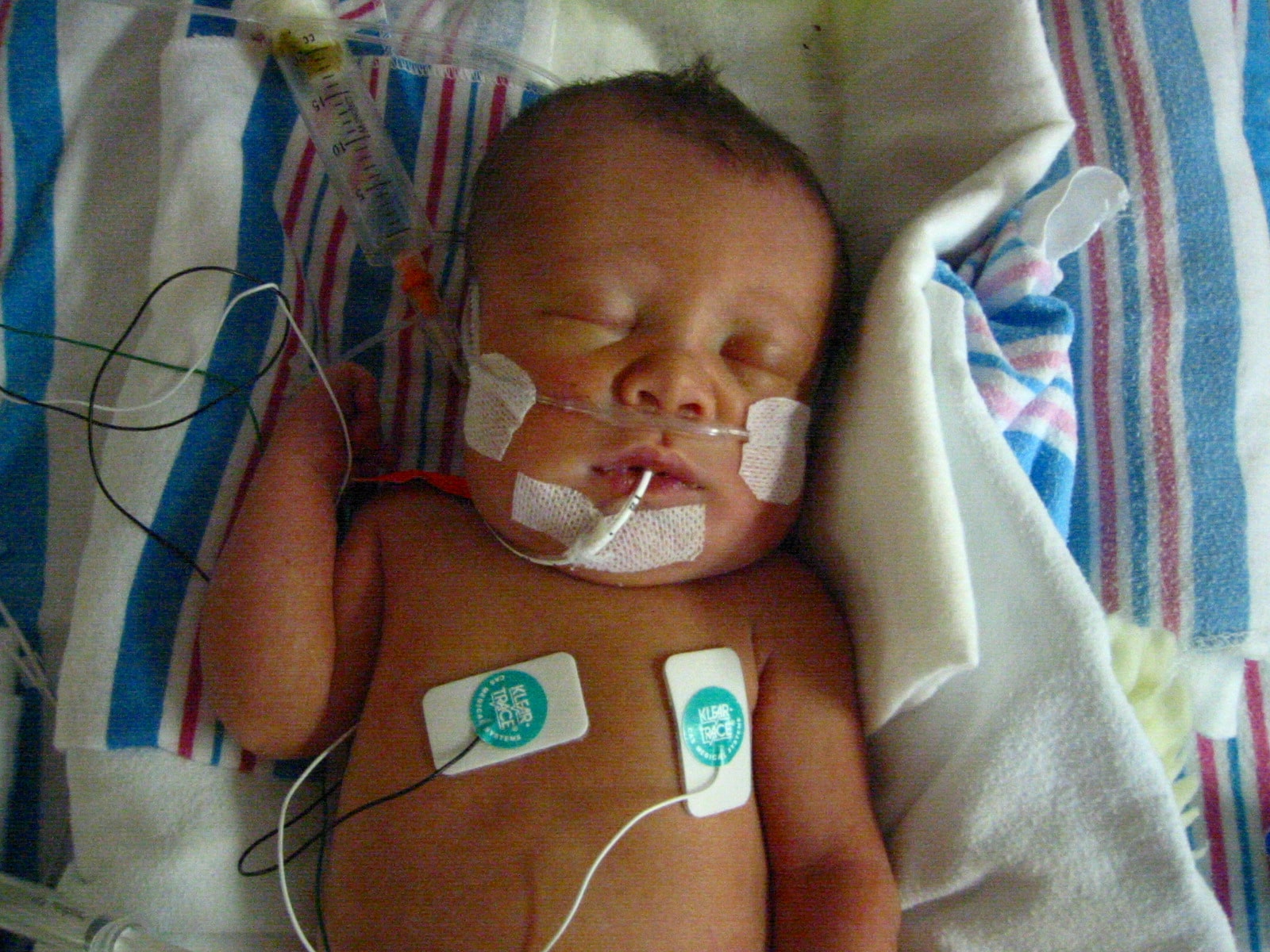
Possible Temporary Maternal Complications
Most women have only temporary but still significant complications such as muscle atrophy, fatigue, constipation, sleep disturbance, depression, and gastric (throat/stomach) irritation.
| Potential Complications | Common Signs/Symptoms | Strategies To Discuss With Doctor & Family | Offsite Links for more info |
|---|---|---|---|
| Constipation - worse if taking medications like ondansetron (Zofran) | Cramps, infrequent or hard stools, abdominal pain, or difficulty passing stools |
| MEDLINEplus: Constipation |
| Fatigue | Inability to work or perform usual activities, often severe |
| |
| Atrophy - wasting or loss of muscle tissue resulting from malnutrition or bed rest | Weakness, fatigue, pain |
| Pregnancy Bed Rest Information |
| Stomach & throat ulcers or irritation | Pain, nausea, food aversions |
| NIDDK: Stomach and Duodenal Ulcers |
| Psychosocial Stress | Depression, anxiety |
| Dartmouth.edu: Depression In Pregnancy PubMed: Obstetrical complications and the development of postpartum depressive symptoms. PubMed: Obstetric, somatic, and demographic risk factors for postpartum depressive symptoms. |
| Sleep Disturbance or Insomnia | Difficulty sleeping |
| MEDLINEplus: Sleeping difficulty |
| Acid Reflux & Heartburn | Throat pain, indigestion, nausea |
| MEDLINEplus: Gastroesophageal reflux disease |
| Gastroparesis - slow movement of food through the stomach/intestines | Sense of fullness after a few bites, nausea/vomiting after drinking/eating a small amount, constipation, reflux, burping |
| NIDDK Info PubMed Case Report |
| Excessive salivation (Ptyalism) | Spitting it out is usually helpful but can worsen dehydration (few if any treatments available) |
| PubMed Case Studies |
| TMJ Trauma - pain or injury to the jaw joint (TMJ or TMD) | Pain or stiffness when opening mouth, headaches, vision changes, clicking noises from jaw. |
|
Severe HG
Weight gain in the mother and adequate growth of the child are used to determine if nutrition is sufficient during pregnancy. Adverse effects of mild HG on the baby do not seem to be common, however, if HG is moderate or severe, there is cause for concern. Severe HG usually causes the mother to rapidly lose an excessive amount of weight, continue to lose weight or gain slowly during the second half of pregnancy, and/or results in a low fetal birth weight or delayed development. Women with prolonged or severe HG are also at greater risk for pregnancy loss, preterm labor and high blood pressure (pre-eclampsia), which may be related to malnutrition and dehydration.
Medical professionals experienced in caring for high-risk pregnancies or women with HG are critical in ensuring adequate care of these mothers.
If a woman shows signs of severe HG and her care seems inadequate or she is not improving, a second opinion by a high-risk OB (maternal-fetal-medicine or perinatologist) is often beneficial.
In most cases, medications and nutritional therapies can ease symptoms and allow both mother and child to avoid serious complications. Read more about severity levels.
Signs Of Severe HG