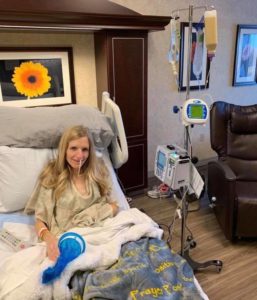
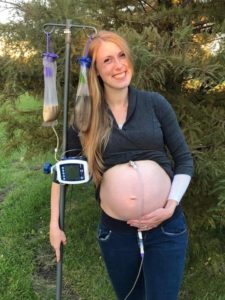
This is not morning sickness.
1 in 3 HG pregnancies does not make it to term. Mothers still die in the 21st Century.

Maternal Complications Due to Hyperemesis
Malnutrition
Acute malnutrition due to lack of macronutrients and micronutrients causes weight loss, muscle wasting, immobility, and other serious complications and may be fatal for both patient and child.
Wernicke's Encephalopathy
Wernicke's encephalopathy is a neurological emergency caused by vitamin B1 deficiencies that must be treated immediately to prevent serious or fatal complications for both patient and child.
Sepsis
According to the CDC, 14.3% of maternal deaths between 2017-2019 were caused by infection or sepsis. HG puts patients at higher risk due to reduced immune function, invasive procedures, and urinary tract infections.
Thiamin Deficiency
Vitamin B1 comes from food and supplements, but is depleted within two weeks of HG, leading to complications which initially share the symptoms of HG and worsen HG but may become life-threatening. Know the signs: changes in vision, speech, gait/movement, cognition, cardiac function, and mood.
Hemorrhage
The risk of hemorrhage is greater in HG due to malnutrition and the changes of pregnancy, plus complications of HG including placental abruption and preeclampsia.
Preterm Labor
Patients with HG have 2x the risk of preterm labor, a 4-fold increased risk of premature birth and are more likely to deliver babies that are small for gestational age and growth restricted likely due to malnutrition and stress.
PTSD
18% of HG patients meet full criteria PTSD compared to 9% of all pregnant patients, and about half of HG survivors have symptoms of trauma due to severe nausea/vomiting, fear of loss, complications, and invasive procedures.
PMADs
1 in 2 HG patients are diagnosed with Perinatal Mood and Anxiety Disorders compared to 1 in 7 of all pregnant patients. The risk increases with severe and prolonged HG symptoms which increase physical and psychosocial challenges.
Embolism
The risk of clotting or embolism increases in pregnancy and is exacerbated by dehydration, malnutrition, and immobility due to HG. Pulmonary embolism is the leading cause of death in pregnancy.
PPCM
According to the CDC, 12.1% of maternal deaths between 2017-2019 were due to peripartum cardiomyopathy. PPCM may occur due to malnutrition in HG and presents as shortness of breath, swelling, rapid weight gain, irregular heartbeat, and chest pain.
Placental Abruption
Women with HG extending beyond the 1st trimester are 3x more likely to have placental abruptions which can lead to life-threatening hemorrhage, preterm delivery, hypoxic encephalopathy and fetal demise.
Fetal Complications
IUGR/SGA
Intrauterine Growth Restriction or Small for Gestational Age is more commonly diagnosed in babies exposed to HG due to malnutrition.
Prematurity
15% of HG pregnancies result in premature birth (a 4-fold increased risk).
Neurological Impact
Children exposed to HG in utero have a 3.3-fold increase in neurodevelopmental issues with the risk increasing with maternal symptoms severity and weight.
Autism Spectrum
Autism spectrum disorders have been found to occur more frequently in children born to mothers who had hyperemesis gravidarum, most likely due to stress, malnutrition, and other factors.
Language Delays
Speech and language delays are more common in children of HG mothers with the risk being greatest in those born to mothers with severe or prolonged symptoms.
Sensory Processing
Many women experiencing severe or prolonged HG, especially those on bed rest late in pregnancy, have children with Sensory Processing Disorder likely due to stress, an immature vestibular system, and malnutrition.
Learning Disabilities
Delays in learning are more common in children of HG mothers with the risk being greatest in those born to mothers with severe or prolonged symptoms.
Mental Health
Children exposed to HG in utero have a 3.6-fold increased risk (38% vs 15% controls) of childhood conduct issues, and double the risk of adult mental health disorders, primarily depression, bipolar disorder, and anxiety.
Adult Cardiometabolic
A significant number of babies exposed to HG in utero will develop chronic cardiac and metabolic issues in adulthood. Findings on this vary.
01
EDUCATE
Learn the risks and complications of HG and how comprehensive, universal assessment and treatment can improve outcomes.
02
AMPLIFY
Amplify the message that 1 MOM is 2 Many to suffer preventable complications and loss due to HG.
03
ADVOCATE
Advocate for state and federal policies that work to eradicate preventable maternal and fetal mortality and morbidity due to HG.